
Get tested for COMT gene mutation here.
What are COMT gene mutations?
COMT (catechol-O-methyltransferase) helps break down certain neurotransmitters and catecholamines, these include dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine.
Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) is important to the areas of the pre-frontal cortex, this area of the brain is involved with personality, inhibition of behaviors, short-term memory, planning, abstract thinking, and emotion/s.
COMT is also involved with metabolizing estrogens. COMT catalyzes the transfer of the methyl-group from SAM to catecholamine substrates, like L-DOPA, dopamine, epinephrine and norepinephrine.
COMT individuals can usually break down these neurotransmitters efficiently. But some COMT individuals may have trouble breaking these chemicals down from impaired function of the COMT enzyme.
With a positive COMT status, we have observed those people may have trouble with methyl donors.
This can lead to irritability, hyperactivity, or abnormal behavior, these people may also be more sensitive to pain. COMT mutations slow the activity of the COMT enzyme which slows dopamine causing dopamine excess imbalances.
COMT is also important in the detoxification of xenobiotics and the metabolism of catechol drugs. COMTV158 is associated with a 3-4 x reduction or increase in activity.
COMT V158M + H62H heterozygous is associated with low or high catecholamines.
COMT V158M + H62H homozygous is associated with high catecholamines and excess estrogen.
COMT problems / Symptoms
- Anxiety
- Social anxiety
- Alcoholism
- Bipolar disorder
- Irritability
- Hyperactivity
- Abnormal behavior
- Psychosis
- Suicidal thoughts
- Negative self-thoughts
- Thyroid abnormalities
- Depression
- Fibromyalgia
- Panic attacks
- Poor libido
- Poor memory
- Hot flushes
- Toxicity
- Schizophrenia
- Fatigue
- P.T.S.D (Post-traumatic stress disorder)
- Allergies
- More sensitive to pain
- Infertility
- Autism
- Hormone imbalances
- Development disorders
- Cancer (Hormone-related)
- Neurological disorders
- Menopausal symptoms
- Andropausal symptoms (male menopause)
*Mental health symptoms in bold.
Reduced tolerance for methyl donors such as:
- 5-MTHF
- Methyl B12
- Caffeine
- SAMe (S-Adenosyl methionine)
- MSM (Methylsulfonylmethane)
- DMG (Dimethylglycine)
- TMG (Trimethylglycine) or Betaine
- CoQ10
- Melatonin
- Quercetin
- Carnitine
- Theanine
- Curcumin
- Green powders/smoothies
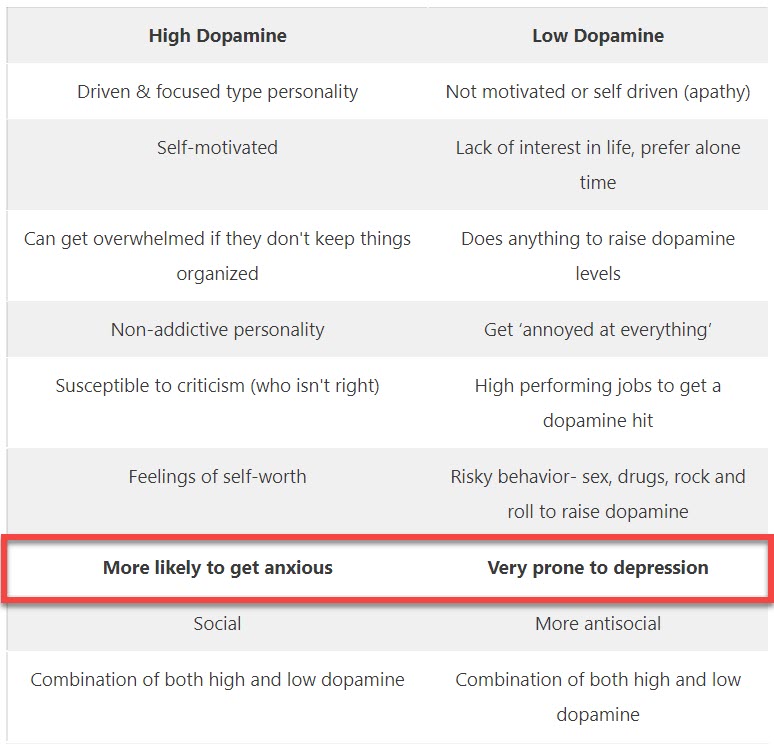
Dopamine disruption from COMT
Because COMT can interfere with dopamine this causes imbalances such as high dopamine or low dopamine.
High dopamine
- Aggression
- Schizophrenia
- Impulsive
- Reckless
- Driven to create situations that stimulate them mentally and physically
- This may lead to violent, destructive or illegal behavior if left unchecked
- Dr’s use antipsychotic medications to reduce a patient’s dopamine levels
Low dopamine
- Addictive tendencies
- Tremors / restless legs
- Low libido
- Lack motivation
- Depression
- Mental exhaustion
- Dull, boring dreams
- Risk of developing alcohol abuse or dependence
Problems with COMTV158
- Associated with violent behavior
- Significantly associated with schizophrenia
- Increased susceptibility to psychosis
- Better performance tests of prefrontal cortex function and working memory
- This means increased tyrosine hydroxylase expression and increased dopamine levels
- COMT V158 – more susceptible to pain
- Affects cognitive function
COMT & allele gene variants
Alleles (An allele is a variant form of a gene).
rs4680(A) = Worrier. Met, more exploratory, lower COMT enzymatic activity, therefore higher dopamine levels, and lower pain. Threshold, enhanced vulnerability to stress, yet also more efficient at processing information under most conditions.
rs4680(G) = Warrior. Val, less exploratory, higher COMT enzymatic activity, therefore lower dopamine levels and higher pain threshold. But better stress resiliency, albeit with a modest reduction in executive cognition performance under most conditions.
(AA allele) = Low activity or higher dopamine which needs certain nutrients for support B6, SAM, magnesium, and FAD.
(G allele) = High activity or lower dopamine which need inhibitors such as quercetin, green tea, and Rhodiola.
Vitamin D & COMT
Vitamin D has previously been shown to influence midbrain dopaminergic neuron function. While increasing the rate-limiting synthetic enzyme for dopamine.
COMT Liver detox – Phase 2
- COMT/TXNRD2 A4251G
- TXNRD2 T2439C
COMT Neurotransmitter Pathway: Serotonin & Dopamine
- COMT61 P199P
- A26166G
- A309G
- C27870T
- C28914T
- A7406G
- C31430T
- C30196T
- G*522A
- G28299A
- T13376G
- T13376G
- H62H
- T24075C
- T26501G
- V158M
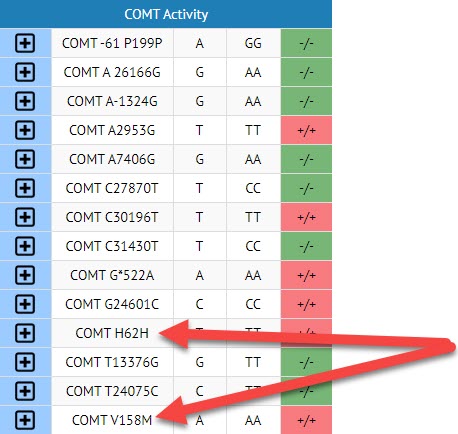
COMT Activity
- COMT61 P199P
- A26166G
- A1324G
- C30196T
- A309G
- A7406G
- C27870T
- C28914T
- T24075C
- C31430T
- G*522A
- G28299A
- H62H
- T13376G
- T26501G
- COMT V158M
Looking for COMT gene mutation treatments, contact us here.

