GAD gene mutation

The GAD gene is needed to convert glutamate which is an excitotoxin into a calming neurotransmitter, you may remember the following table that shows the conversion from glutamate to glutamine to GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid):
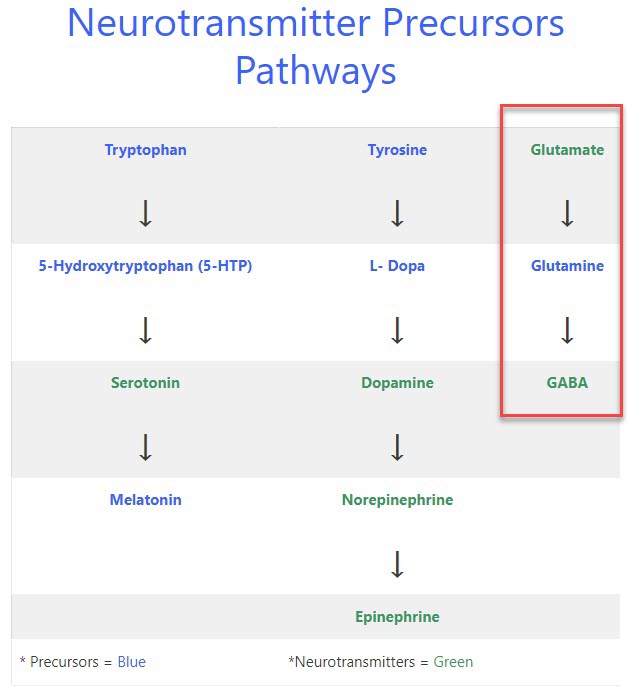
Notice the words “calming neurotransmitter”, how important is that, when you have so many people who just can’t calm down e.g.
GABA deficiency
- Anxiety
- Panic attacks
- Mania
- OCD
- Hyperactivity
- Psychosis
- Irritability
- Can’t relax
- Constantly stressed
- Can’t sleep well
- Aggression
- Can’t let go
- Overly worried
- Can’t cope
- Agitated
- Tension
- Seizures
To best understand the power of GABA, it’s the main reason people drink alcohol and or use heroin, because these substances temporarily make more GABA, the result is the ability to calm down.
When there are mutations in GAD, a person may not make enough GABA and so excitatory neurotransmitters get the advantage over the calming neurotransmitters, the result can be all of the above symptoms and many of the symptoms associated with the COMT and MAO genes related to mental health problems.
Take a look at this example:
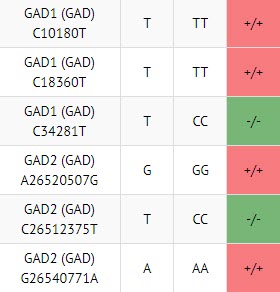
As you can see, the above images show 4 homozygous (double gene mutations) of a total of 6 genes, in this example it could be said that this person likely makes 60% less GABA with these gene mutations. If you were to apply this idea, it means this person is 60% less likely to be able to remain calm, that’s a big problem, especially if you have other genes in COMT, MAO, MTHFR that are driving up your excitatory neurotransmitters, that is a sure combination for many mental health problems.

