Methylation is one of the most important processes that happen in your brain and body. It makes everything work properly and without the process of methylation, you cannot live. Methylation is the process of maintaining the balance of literally thousands of neurotransmitters, hormones and other biochemicals essential to good health and life.
Methylation is so important in fact that it is responsible for millions of “methylation” reactions every second! So its really important to understand that your ability to “methyl-ate” is a vital factor in determining your ability to achieve good health and well being both mentally and physically. Methylation has many jobs to do, it does this by supplying the body and its various system with what they need to do their job at optimal levels, so when your methylation is out of balance this can set off a chain reaction of problems that can literally mean the difference between life and death.
Methylation is produced in the body to make methyl groups, these groups are then “donated” to the parts in the body and mind that need them for processing their many functions such as:
- Turn genes on and off
- Building & repairing DNA and RNA
- Reduce the aging process
- Reduce your risk of heart attack and strokes by 75%.
- Balance your homocystenine
- Deal with stress
- Maintain good mental health
- Process hormones
- Detoxify chemicals & heavy metals
- Fighting infections
- Building immune cells
- Balance histamine
- Support neurotransmitters to prevent depression, anxiety and mental health disorders
- Produce powerful antioxidants
- Works with vitamins, minerals, essential fats and amino acids
As you can see methylation has many jobs to do, so its vital if your unwell that you check on the health of your methylation cycle.
Symptoms of methylation imbalances
So, how do you know if your methylation is working properly? Signs and symptoms of methylation problems can tell us if we have imbalances in methylation. The key to good methylation is balance so when your methylation is having some trouble maintaining this balance certain symptoms can appear. When methylation becomes unbalanced you can end up usually in one of two categories, you can have symptoms of under-methylation from not making enough methylation and or you can have symptoms related to over-methylation. Some people have symptoms in both under and over methylation.
Under-methylation symptoms
- ADD/ADHD
- (Addictive) behavior
- Allergic reactions
- Bulimia
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Anxiety
- Cancer
- Autism
- Autoimmune disease
- Bipolar disorder
- Aging
- Anorexia
- Chronic degenerative diseases
- Cardiovascular disease
- Delusions
- Cleft palate
- Diabetes
- Chronic fatigue
- Down’s syndrome
- Depression
- Poor detoxification
- Fibromyalgia
- Headaches
- Infertility
- Joint stiffness, pain, swelling
- Insomnia
- Muscle pains
- Low neurotransmitters
- Obesity or weight gain
- Obsessive-compulsive disease
- Phobias
- Oppositional defiant disorder
- Pain
- Psychosis
- Schizophrenia
- PCOS
- Recurrent pregnancy loss, miscarriage
- Thyroid dysfunction
Over-methylation symptoms
- Headache
- Migraine
- Rashes
- Irritability
- Increase in anxiety
- Joint pain
- Muscle pain
- Insomnia
- Depression (Maybe suicidal)
- Nausea
- Seizures
- Schizophrenia
- Vomiting
- Stomach pain
- Sweating
- Rash
- Hypokalemia
- Heart palpitations
Causes of methylation imbalances
The are many things that can interfere with methylation, lifestyle, nutrition, the environment you live in and genetics play a big role in how well you methyl-ate or not. The main causes of methylation include:
- Genetic mutations such as in MTHFR and other associated gene mutations
- MTHFR Gene mutations C667T & A1298C
- Nutritional problems
- Stress (Mental & physical)
- Environmental chemicals & toxins
- Heavy metal toxicity
- Medications (antacids, methotrexate, metformin, nitrous oxides, antiseptics)
- Reduced hydrochloric acids for digestion
- Aging (as we age methylation can reduce)
- Diet
- Alcohol
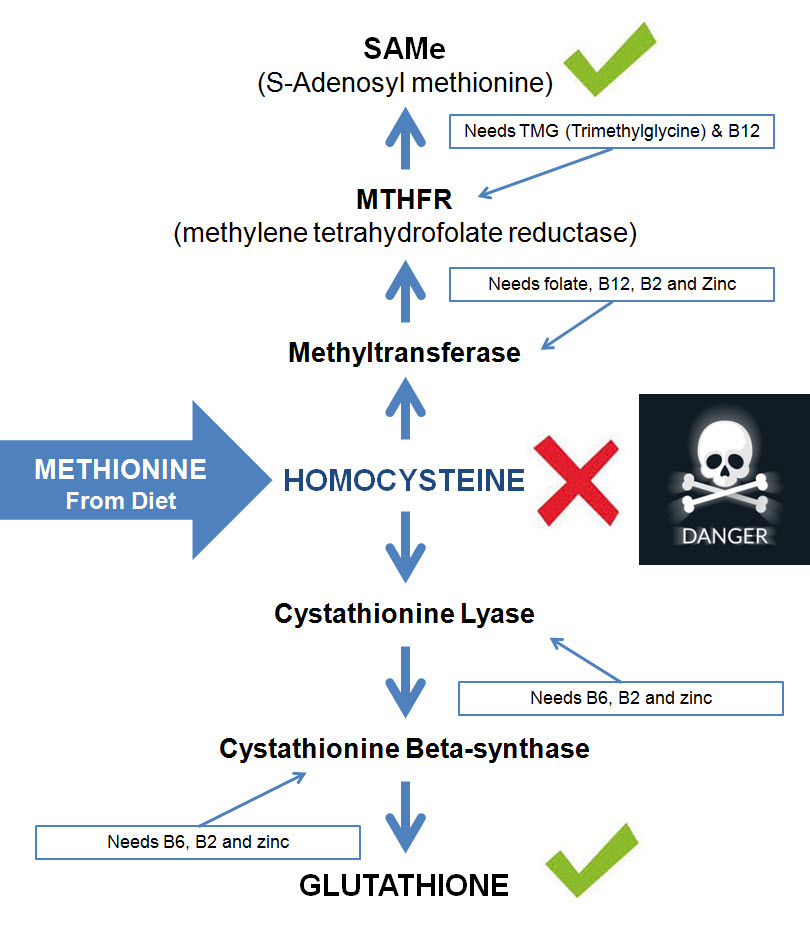
The importance of homocysteine in methylation
One the more important methylation processes is called the homocysteine cycle, this process is vital in keeping us healthy and so having homocysteine out of balance can mean big problems, this is because homocysteine needs to be converted to SAMe (at the top) and glutathione (at the bottom) as per the diagram below. Should something from the list above interfere with this process, methylation of homocysteine is inhibited which can lead to imbalances in the methylation cycle that can lead to disease and death.
If the is done right, SAMe goes on to be a methyl donor to support healthy methylation and glutathione goes on to act as a powerful antioxidant that prevents the aging process.
Methylation & MTHFR gene mutations
People with mthfr gene mutations often have problems with methylation that need to be corrected and supported. One of the biggest problems that comes with the mthfr gene mutation is the reduced ability to convert folate, into methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR), which is the enzyme needed in many parts of the methylation process. Further this reduced ability to use folate properly, means that many other supportive nutrients involved in the methylation cycle are also disadvantaged, which is why those with the mthfr gene mutations need additional support to ensure that their methylation cycle is corrected and maintained to prevent methylation symptoms and diseases that result from methylation imbalances.
Methylation is complex to say the least, if you have any of the symptoms on this page it is best to contact one of our professionals who understand methylation and how to correct imbalances.


